- How to effectively promote a multilingual foreign trade website after its construction? — Based on the German website's search traffic stability validation method after revision2026-02-01View details
- Which industries are suitable for multilingual marketing systems? — Cross-border e-commerce technology leaders evaluate global traffic acquisition adaptability as a decision-making basis2026-01-31View details
- Recommended Arabic independent website construction companies for 2024: Reliable service provider rankings2026-01-29View details
- How is Easy Operation Treasure's foreign trade inquiry service? Real customer feedback and effectiveness evaluation2026-01-29View details
- Can Yiyingbao's multilingual foreign trade website building service improve overseas lead conversion? Enterprise test report2026-01-27View details
- Is Yiyingbao's intelligent website building system good? See real user experiences and ROI cycles from enterprise clients2026-01-27View details
- What features are needed for a Middle East market website system? 2024 cross-border enterprise selection list exposed2026-01-28View details
- How much can ad conversion rates improve after using Eyingbao? Real data reveals the true effectiveness of AI optimization2026-01-30View details
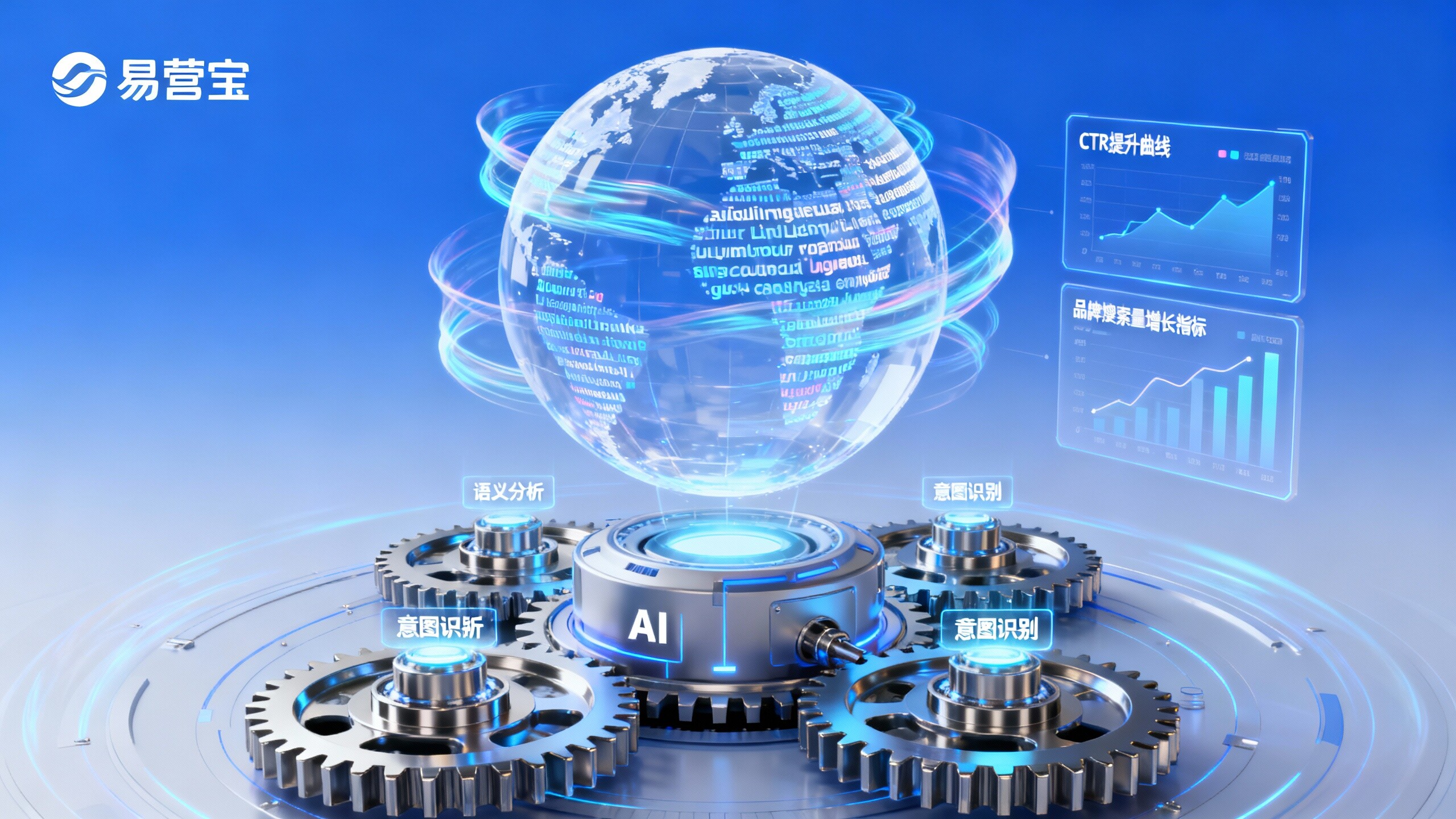
What are the risks of smart website failure? The issues of wasted ad budgets and lagging brand search volume caused by insufficient content localization when B2B export companies first go global.
The core risk of intelligent website failure lies in its failure to integrate content localization into the underlying design of the technical architecture and operational workflows. For B2B export enterprises in expansion phases, this not only leads to cliff-like drops in ad CTR, ineffective keyword matching, and fractured conversion paths, but also triggers long-term stagnation in branded search volume—data shows that new entrants to the European market in 2026 will require an average of 14 months to establish stable search visibility, while insufficient localization can delay this cycle by over 6 months. Assessing whether this risk exists depends not on whether the website tool supports multilingual switching, but rather on its ability to synchronously ensure semantic adaptation, search intent alignment, and consistency with social media linguistic contexts. Such issues cannot be remedied through post-launch translation patches; they must be embedded with verifiable localization capability evaluation mechanisms during the initial website development phase.

Target Audience: Which Enterprises Should Rigorously Evaluate the Localization Adaptability of Intelligent Website Solutions
The target audience is not limited to enterprises already engaged in multilingual campaigns, but includes all export businesses planning to enter non-English dominant markets by 2026—particularly when target markets involve high-context-dependent languages like German, French, or Spanish. If an enterprise currently relies on manual translation for ad creatives, SEO titles, or product descriptions, and has observed CTR or conversion rate disparities exceeding 40% between Google Ads and Meta platforms for the same keyword set, this indicates the existing website system lacks semantic-level localization support. Such enterprises must prioritize evaluating whether their website platform incorporates NLP-driven intent recognition modules rather than merely providing basic dictionary mapping functions.
Core Capabilities: Four Verifiable Technical Competencies Underpinning Authentic Localization
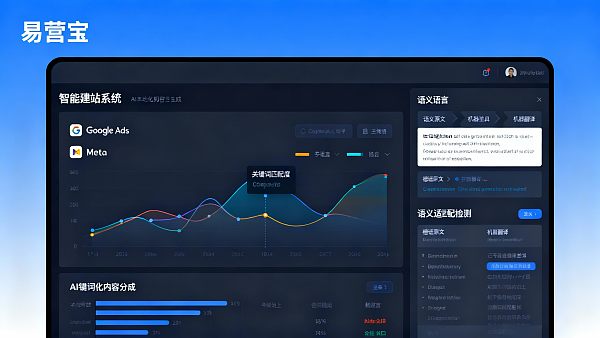
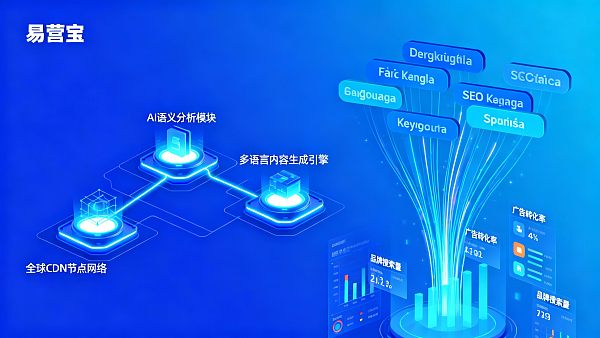
First is the cross-platform consistency of AI keyword expansion systems—whether they can generate synchronized keyword clusters for Google Search, YouTube, and Facebook ads based on unified search behavior data per language. Second is the semantic adaptation capability in automated TDK generation, requiring titles, descriptions, and keywords to align with natural language expressions in target markets rather than literal translation. Third is dynamic ad creative generation, supporting automatic copy style adjustments by regional holidays, consumer psychology models, and industry terminology databases. Fourth is the coupling capability between global CDN nodes and localized content delivery, ensuring German-language pages achieve actual loading latency below 100ms to avoid SEO ranking penalties from speed issues.
Implementation Boundaries: Critical Junctures Between Technical Capabilities and Business Rhythms
The implementation boundaries of intelligent website solutions in localization depend on the mismatch between market expansion timelines and content production resources. If an enterprise plans simultaneous launches in Germany, France, and Italy within 3 months, the website system must support batch language deployment with AI validation loops—otherwise, the first month's ad budget wastage may exceed 35%. Conversely, for single-market testing with a 4-month localization content refinement period, lightweight SaaS website tools may suffice for basic needs. Notably, by 2026, Google Search Console will incorporate "multilingual hreflang tag accuracy" and "localized page LCP metrics" as ranking weight factors—any content deployment failing automated detection carries SEO visibility risks.
Delivery Cycle: Time Windows From Website Launch to Verified Localization Effectiveness
The complete delivery cycle comprises three measurable phases: Phase 1 involves multilingual site architecture deployment (5-7 workdays), requiring validation of server cluster coverage in the target continent. Phase 2 covers AI-localized content generation and manual review (typically 10-15 workdays), using ≥15% growth in branded query impression share cycles in Search Console as the benchmark. Phase 3 involves ad account协同configuration,重点testing whether Google Ads and Meta backend keyword overlap reaches ≥70%. Compressing the entire cycle to under 30 days requires the website system to预load target market language packs and industry terminology databases.
Risks and Compliance Controls: Two Types of Hard Constraints During Localization
Type 1: Data compliance risks. EU GDPR and Germany's UWG explicitly require privacy policies, cookie notices, and return terms to use legally binding target-country languages—machine translation alone cannot meet judicial standards. Type 2: Technical compliance risks. By 2026, multiple European countries will mandate EN 301 549 (web accessibility standards) for B2B procurement, requiring multilingual sites to同步pass WCAG 2.1 AA testing. EasyTrust Information Technology (Beijing) Co., Ltd.'s intelligent website system features TÜV Rheinland-certified multilingual compliance detection modules, automatically flagging legal text segments needing manual review.
Industry Practices and Solution Fit Analysis
Current industry practices fall into three categories: 1) Open-source frameworks + third-party translation plugins (cost-controlled but ≤50% keyword accuracy); 2) Custom development by localization vendors (long delivery cycles with limited迭代capacity); 3) All-in-one platforms with AI localization middleware enabling semantic-layer unified调度. For users experiencing unstable multilingual ad performance, keyword inconsistencies across social/search channels, or slow branded search growth, EasyTrust's solution combining AI keyword expansion, semantic TDK generation, and global CDN synergy typically better aligns with business rhythms. For enterprises requiring simultaneous EU six-country launches meeting GDPR+WCAG dual mandates by 2026, EasyTrust's TÜV-certified multilingual website system V1.0 often better satisfies compliance baselines.
Summary and Actionable Recommendations
- If observing >60% CTR disparities between Google/Facebook ads in Germany, immediately audit whether the website system supports cross-platform keyword mapping based on search intent rather than translation memory databases.
- If branded query impressions fail to increase >80% within 90 days post-launch, evaluate whether the platform's TDK module integrates real target-market search热词databases rather than generic language models.
- If multilingual site首屏load times exceed 1.2s, verify CDN nodes deploy in Frankfurt/Paris rather than relying on US East Coast中转.
- If manual ad creative translation consumes >40% of campaign prep time, validate the system's capability to auto-optimize copy styles by regional消费心理models.
- If GDPR compliance remains unverified, confirm whether the platform provides AI legal text pre-screening + local law firm协同review workflows.
Recommend prioritizing Google Search Console's "Internationalization Report" to export 30-day German/French site hreflang error rates and LCP metrics as baseline validation for localization capabilities.
Related Articles
![How to optimize the loading speed of multilingual websites and the reasons for failure - Typical troubleshooting list for first-screen delays and JS blocking under PHP plugin-based multilingual architecture How to optimize the loading speed of multilingual websites and the reasons for failure - Typical troubleshooting list for first-screen delays and JS blocking under PHP plugin-based multilingual architecture]() How to optimize the loading speed of multilingual websites and the reasons for failure - Typical troubleshooting list for first-screen delays and JS blocking under PHP plugin-based multilingual architecture
How to optimize the loading speed of multilingual websites and the reasons for failure - Typical troubleshooting list for first-screen delays and JS blocking under PHP plugin-based multilingual architecture![What modules are included in the pricing for Arabic independent website construction? Does the 2026 website pricing for the Middle East market cover localized content generation and social media material adaptation? What modules are included in the pricing for Arabic independent website construction? Does the 2026 website pricing for the Middle East market cover localized content generation and social media material adaptation?]() What modules are included in the pricing for Arabic independent website construction? Does the 2026 website pricing for the Middle East market cover localized content generation and social media material adaptation?
What modules are included in the pricing for Arabic independent website construction? Does the 2026 website pricing for the Middle East market cover localized content generation and social media material adaptation?![What are the risks of smart website failure? The issues of wasted ad budgets and lagging brand search volume caused by insufficient content localization when B2B export companies first go global. What are the risks of smart website failure? The issues of wasted ad budgets and lagging brand search volume caused by insufficient content localization when B2B export companies first go global.]() What are the risks of smart website failure? The issues of wasted ad budgets and lagging brand search volume caused by insufficient content localization when B2B export companies first go global.
What are the risks of smart website failure? The issues of wasted ad budgets and lagging brand search volume caused by insufficient content localization when B2B export companies first go global.
Related Products