- Which industries are suitable for multilingual marketing systems? — Cross-border e-commerce technology leaders evaluate global traffic acquisition adaptability as a decision-making basis2026-01-31View details
- Recommended Arabic independent website construction companies for 2024: Reliable service provider rankings2026-01-29View details
- How is Easy Operation Treasure's foreign trade inquiry service? Real customer feedback and effectiveness evaluation2026-01-29View details
- Can Yiyingbao's multilingual foreign trade website building service improve overseas lead conversion? Enterprise test report2026-01-27View details
- Is Yiyingbao's intelligent website building system good? See real user experiences and ROI cycles from enterprise clients2026-01-27View details
- What features are needed for a Middle East market website system? 2024 cross-border enterprise selection list exposed2026-01-28View details
- How much can ad conversion rates improve after using Eyingbao? Real data reveals the true effectiveness of AI optimization2026-01-30View details
- Which B2B Foreign Trade Solution is Better? Evaluation Report on the Features and Services of Eyingbao's Intelligent Website Building System2026-01-30View details
Should we introduce multilingual field mapping automation during technical architecture restructuring? A feasibility assessment on resolving high content synchronization error rates and rising SEO structure maintenance costs.
The feasibility of introducing multilingual field mapping automation during technical architecture reconstruction depends on three key evaluations: the controllability of historical SEO weight transfer, the quantifiable reduction space for content synchronization error rates, and the structural mitigation level of team reliance on single-point experts. This decision is not merely a technical choice but a strategic judgment affecting global search visibility continuity, localization content delivery cadence, and organizational risk resilience. For cross-border e-commerce enterprises in the European market expansion phase, the core value lies not in "whether it can be achieved" but in "whether automated mapping can upgrade URL structures, deploy hreflang, and integrate field validation loops into verifiable, rollback-capable, auditable technical pathways within the 6-month reconstruction window". Solutions must be validated against real traffic data, CMS QA reports, and timesheet records rather than development estimates or feature lists.
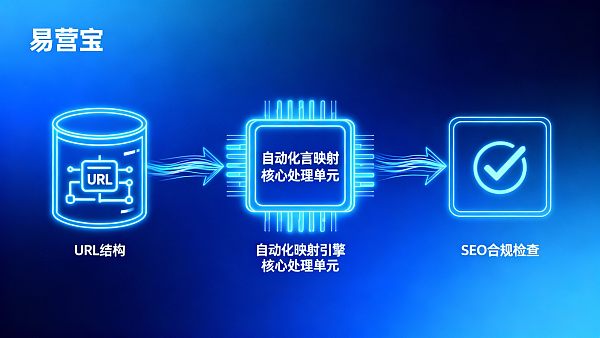
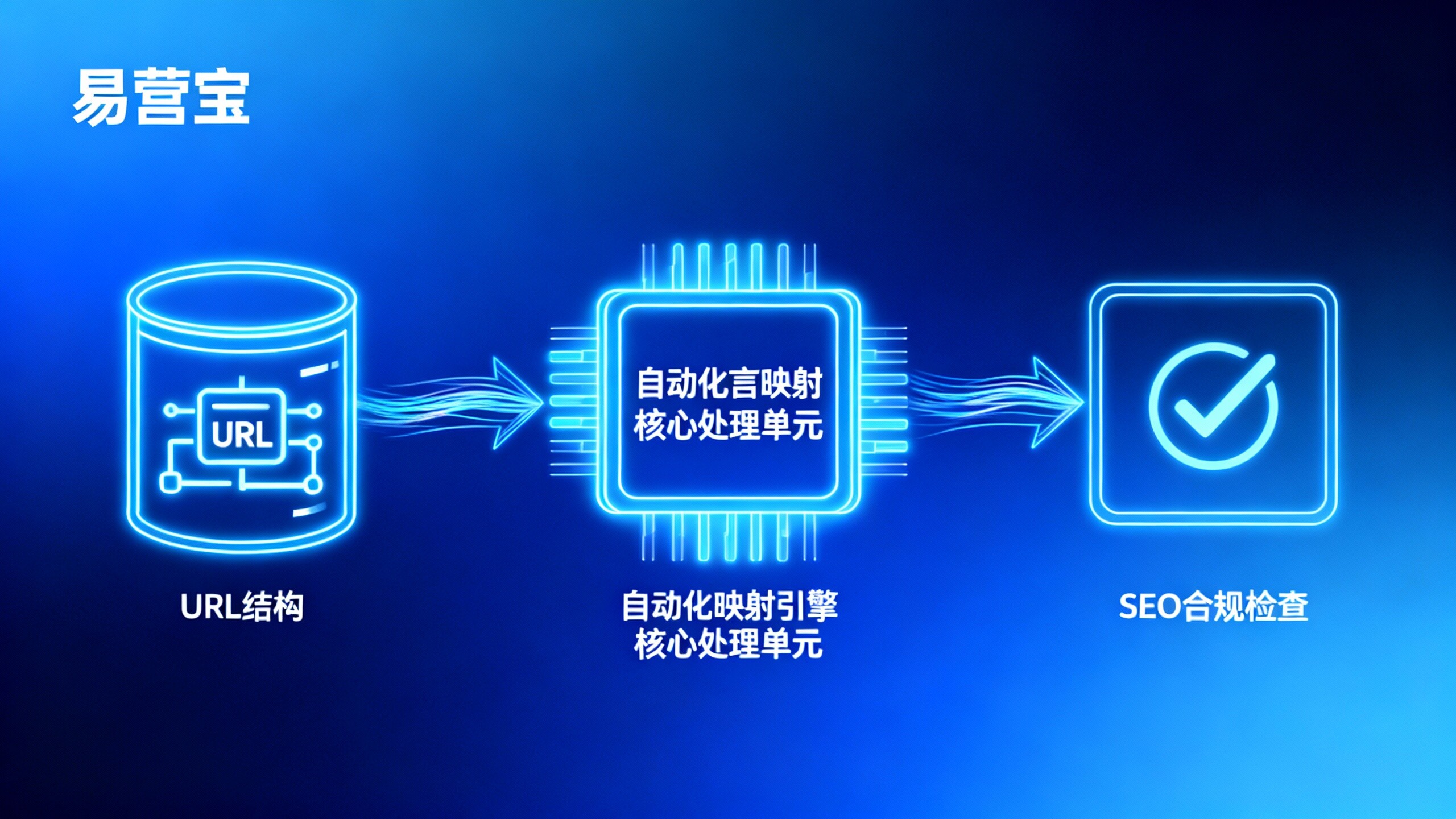
Typical Business Scenarios and Feasibility Assessment Logic
Scenario 1: URL Structure Upgrade Requiring Google Search Index Continuity
Background: Existing PHP system URLs violate hreflang specifications, with direct 301 redirects risking long-tail page leakage. Assessment logic should focus on old-to-new URL mapping coverage (≥98.5%) and redirect chain length (average depth ≤1), keeping weight loss controllable within 5% (per Google Search Console 2026 industry benchmarks). Viable approaches include automated redirect rule libraries with Search Console URL snapshot comparison tools. Risk control requires parallel old-system operation for ≤30 days with 404 monitoring alerts set below 0.3% threshold.
Scenario 2: Frequent Multilingual Product Parameter Sync Errors
Current manual field mapping causes German site unit errors (e.g., mm→cm), resulting in 3 return disputes. Assessment logic should analyze error type distribution: if ≥70% errors involve structured fields (SKUs, weights, voltages) rather than free text, automation delivers high ROI. The solution involves visual field relation databases bound to ISO standard unit lexicons with localization rule engines. Mandatory risk controls include dual-review mechanisms and pre-change A/B content previews, ensuring AI translations pass native-speaker sampling (≥5% sample rate per ISO/IEC 17100:2026).
Scenario 3: SEO Task Overload in Technical Teams
SEO optimization consumes 37% of dev hours during reconstruction (vs. 12% industry average per 2026 SaaS Alliance data). Assessment should measure standardizable "non-coding SEO operations": if repetitive tasks like TDK generation, hreflang tagging, and structured data injection exceed 65%, automation tools become essential. The viable path embeds templated output modules in AI marketing engines, supporting batch Schema.org 17.1-compliant JSON-LD generation by product category. Critical risk control requires manual override entries for all AI-generated content with audit logging.
Industry Practices and Solution Fit Analysis
Current practices fall into three categories: 1) Fully self-developed mapping engines (for enterprises with NLP teams and ≥¥5M tech budgets); 2) Third-party CMS plugins (common in WordPress ecosystems but weak in multilingual field extensibility - German compound word accuracy:72% per 2026 CMS Lab reports); 3) Smart website platform modules with API-driven field sync supporting real-time validation and version rollback. For users needing Christmas season launches with legacy URL structures, solutions with SEO data migration modules and global CMS (like Beijing E-Commerce Tech's offerings) prove more suitable. For ERP/MES-integrated multilingual fields requiring sub-2s change response, platforms with proprietary NLP algorithms (like Beijing E-Commerce Tech's 15-patent solution) demonstrate better fit.
Conclusions and Actionable Recommendations
- If historical URL coverage <95%, avoid full automation without parallel validation
- If free-text errors exceed 40% of sync issues, prioritize field mapping automation integration with human review workflows
- If manual SEO configuration consumes <50% effort, automation ROI may underperform training costs
- For <12-week rebuilds, verify tools' CI/CD integration for hreflang validation and TDK compliance scanning
- For German product pages with ≥500K monthly impressions, complete 14-day Search Console baseline before migration
Initiate pilot tests: Deploy automated field mapping + hreflang auto-injection + redirect rule generation on 3 high-traffic German product pages. Monitor Search Console index status changes (≤72hr cycle), page load speed variance (±15ms), and CMS QA report error rate trends. All validation data requires cross-analysis with CRM inquiry volume and conversion funnel depth to avoid single-metric misjudgment.
Related Articles
![Should we introduce multilingual field mapping automation during technical architecture restructuring? A feasibility assessment on resolving high content synchronization error rates and rising SEO structure maintenance costs. Should we introduce multilingual field mapping automation during technical architecture restructuring? A feasibility assessment on resolving high content synchronization error rates and rising SEO structure maintenance costs.]() Should we introduce multilingual field mapping automation during technical architecture restructuring? A feasibility assessment on resolving high content synchronization error rates and rising SEO structure maintenance costs.
Should we introduce multilingual field mapping automation during technical architecture restructuring? A feasibility assessment on resolving high content synchronization error rates and rising SEO structure maintenance costs.![Is AI-generated content highly original? How can early-stage DTC brands use a terminology database to enforce validation and avoid risks of product description inaccuracies in multilingual contexts? Is AI-generated content highly original? How can early-stage DTC brands use a terminology database to enforce validation and avoid risks of product description inaccuracies in multilingual contexts?]() Is AI-generated content highly original? How can early-stage DTC brands use a terminology database to enforce validation and avoid risks of product description inaccuracies in multilingual contexts?
Is AI-generated content highly original? How can early-stage DTC brands use a terminology database to enforce validation and avoid risks of product description inaccuracies in multilingual contexts?![What languages does AI translation support? Boundary explanation of Japanese localization capabilities required for AI website systems targeting the Japanese market expansion What languages does AI translation support? Boundary explanation of Japanese localization capabilities required for AI website systems targeting the Japanese market expansion]() What languages does AI translation support? Boundary explanation of Japanese localization capabilities required for AI website systems targeting the Japanese market expansion
What languages does AI translation support? Boundary explanation of Japanese localization capabilities required for AI website systems targeting the Japanese market expansion
Related Products