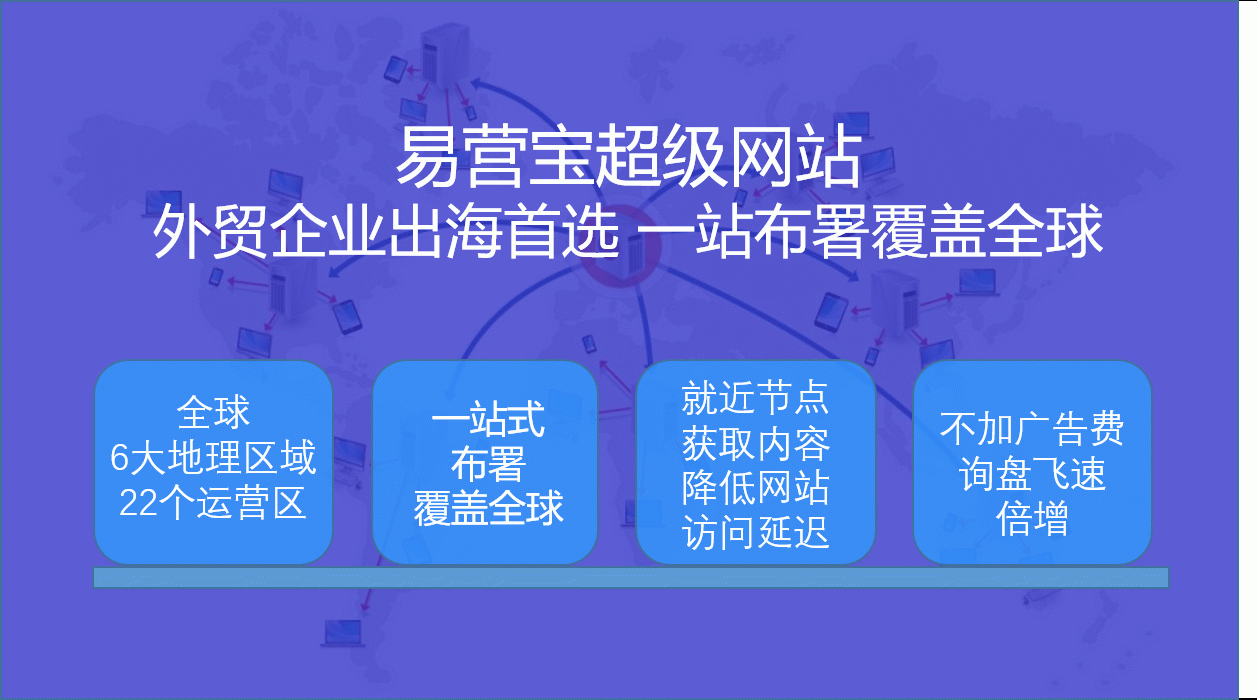
Definition of a Multilingual Website: Digital Assets That Cross Language Barriers
A multilingual website (Multilingual Website) refers to a website whose content is presented in two or more language versions, aimed at serving users from different language groups. It overlaps with the concept of a multi-regional website (Multi-regional Website), but its core lies in language.
An excellent multilingual website should provide:
Linguistic Localization: Ensure accurate text translation, conforming to the grammar and expression habits of the target language.
Cultural Adaption: Adjust content, images, date formats, currencies, and user interface (UI) elements to align with the cultural preferences of the target market.
SEO Friendliness: Ensure search engines can identify, crawl, and correctly index each language version and display it to the corresponding language users.
Multilingual Website vs. Machine Translation
The essence of a multilingual website lies in localization, not just translation. Simple machine translation may lead to:
SEO Failure: The quality and keyword selection of machine translation often do not align with the search habits of the target language.
Loss of Professionalism: Stiff or incorrect translations can damage the brand's image in professional fields.
Low Conversion Rates: Interfaces that do not adapt to local culture and user habits can lead to user loss.
The Development History of Multilingual Websites: From Language Directories to Smart AI Localization
The evolution of multilingual websites is an inevitable result of global business demands and internet technological advancements:
1. Early Stage: Content Duplication and Maintenance Bottlenecks (1990s-2000s)
In the early days of the internet, multilingual websites were typically created by simply copying HTML files and placing different language versions in separate directories.
Pain Points: Extremely high maintenance costs, difficult content updates, and search engines struggling to accurately identify language relationships.
2. Technical Standardization and CMS-Driven (2005-2012):
Rise of CMS: Content management systems (CMS) like WordPress and Drupal began offering multilingual plugins and solutions, simplifying content management.
Birth of
hreflangTags: This was a milestone in the development history of multilingual websites. In 2011, Google introduced thehreflangtag, allowing webmasters to explicitly tell search engines that a specific page is a language or regional alternative version of another page, solving SEO issues caused by content duplication.
3. Mobile and Globalization Acceleration (2013-2018):
Mobile-First: Multilingual websites had to adapt to responsive design for mobile devices.
CDN Popularization: **Content Delivery Networks (CDNs)** were widely used for multilingual websites, ensuring fast access for users in different regions.
Google Algorithm Maturity: Google's Penguin, Panda, and other algorithm updates further penalized low-quality machine-translated content, emphasizing translation quality and user experience.
4. AI Smart Localization and Full-Channel Marketing (2019-Present):
AI Translation Integration: The introduction of neural machine translation (NMT) and large language models (LLMs) significantly improved the quality of initial translations, but **post-editing** remains indispensable.
Full-Channel Marketing: Multilingual websites are deeply integrated with global SEO, local paid ads (e.g., Google Ads, Bing Ads), and local social media marketing, achieving closed-loop management from traffic to conversion.
Web Performance Optimization: Focus on Core Web Vitals for multilingual websites, ensuring fast user experiences across all language versions.
Technical Principles of Multilingual Websites: SEO Structure and hreflang Protocol
The success of a multilingual website entirely depends on its underlying technical structure and strict adherence to search engine guidelines.
1. Core Structure: Choosing the URL Architecture
Correctly choosing the URL architecture is the first step in multilingual SEO. There are three recommended patterns:
Do not use URL parameters (e.g., site.com/?lang=de), as they are difficult for search engines to accurately crawl and index.
2. The Ultimate Weapon for Solving Duplicate Content: hreflang Tags
hreflang is an HTML tag attribute used to tell search engines: “This page is a language/regional alternative version of another page.”
Functions:
Targeting: Ensure Spanish users see Spanish pages in search results, not Chinese pages.
Avoiding Penalties: Clearly inform search engines that this is not duplicate content, thus avoiding SEO penalties.
Technical Implementation:
HTMLhreflangmust be implemented in a bidirectional reference manner. For example, a Chinese page must reference the Spanish page, and the Spanish page must also reference the Chinese page.<link rel="alternate" hreflang="es" href="http://site.com/es/page.html" /> <link rel="alternate" hreflang="zh-Hans" href="http://site.com/zh/page.html" /> <link rel="alternate" hreflang="x-default" href="http://site.com/" />
3. Content Delivery and Speed: CDN and Local Hosting
Multilingual websites often target global users, making **website loading speed (LCP, TTFB)** crucial:
Global CDN: Deploy a global content delivery network (CDN) to cache static resources of different language versions at the edge nodes closest to users.
Local Hosting: For ccTLD structures, host the website on servers in the target country or region to effectively reduce TTFB (Time to First Byte) for that area.
Technical Features and Localization Strategies of Multilingual Websites
An efficient multilingual website requires combining technical details with deep localization strategies.
1. Localized Keyword Research (Localized Keyword Research)
Feature: Successful localization is not simply translating keywords but conducting search intent research in the target language. For example, the term “mobile phone” may have different search popularity and user expressions in different countries.
Strategy: Use tools like Google Keyword Planner and SEMrush to research the search volume, competition, and conversion intent of target language users and integrate them into titles, content, and meta descriptions.
2. Avoiding Auto-Redirect Traps
Issue: Many websites force auto-redirects based on users’ IP addresses. For example, users in the U.S. are forcibly redirected to the English site even if they want to view Chinese content.
Consequence: This is highly detrimental to SEO, as it prevents search engine crawlers (often from U.S. IPs) from accessing and indexing other language versions.
Strategy: Always allow users to manually select the language (via a visible, easy-to-find language switcher), offering only suggestive recommendations, not forced jumps.
3. Localized Content Elements
Currency and Payments: Ensure prices are displayed in local currencies and integrate mainstream local payment gateways.
Dates and Times: Formats should match local habits (e.g., MM/DD/YYYY in the U.S. vs. DD/MM/YYYY in Europe).
Legal Compliance: Privacy policies, cookie pop-ups, GDPR/CCPA compliance statements must be translated and adjusted according to the target country’s laws.
4. Language Environment and Cultural Adaptation
Images and Videos: Use images that align with the target culture and avoid causing offense. For example, certain gestures may have entirely different meanings in different cultures.
Localized Service Information: Clearly display local contact methods, phone numbers (using local codes), and business hours.
Deep Applications and Business Value of Multilingual Websites
Multilingual websites are core tools for achieving global business growth and brand authority:

Global B2B Business Expansion:
Value: Through localized websites, professionally showcase product manuals, technical specifications, and case studies to directly acquire high-quality international business leads.
Application: Use subdirectory structures to provide German, French, and Italian versions for different European markets.
Cross-Border E-Commerce and Independent Sites:
Value: Solve trust issues before purchase by displaying prices in local currencies, product descriptions in local languages, and customer service, significantly improving international order conversion rates.
Application: Deploy
hreflangtags on product detail pages to ensure each SKU is accurately indexed by Google Shopping ads and organic search in the target market.
Content Marketing and Brand Authority Building:
Value: Translate core blogs and white papers into local languages to quickly establish **thought leadership** and brand authority in the target market.
Application: Hire professional post-editors or local copywriters to polish AI-translated drafts, ensuring content professionalism and cultural fit.
EasyProfit: Your Multilingual Website and Global SEO Strategy Partner
EasyProfit deeply understands the complexity of multilingual websites and the nuances of SEO strategies. Our services go beyond simple translation, offering a global content asset management and conversion solution:
hreflangTag Audit and Deployment: Thoroughly inspect and correctly deployhreflangtags, solving core technical challenges of multilingual SEO to ensure accurate Google indexing.Global Keyword Localization Research: We don’t translate keywords; we research them anew. Ensure your target language versions use high-conversion keywords actually searched by local users.
Technical Architecture Optimization: Help you choose the most suitable URL structure (ccTLD, subdirectory, subdomain) for your business and optimize server and CDN configurations for global access speed.
AI-Assisted Localization Workflow: Combine advanced AI translation technology with professional human post-editing to ensure content high translation quality, fast speed, and controllable costs.
Multilingual Conversion Rate Optimization (CRO): Adjust UI elements, CTAs (call-to-action), and payment flows to target market cultures, maximizing local users’ purchase intent.
FAQ
1. Where should the hreflang tag be placed? What language codes should I use?
The hreflang tag can be placed in three locations:
HTML
<head>section (most common).HTTP response header (suitable for non-HTML files like PDFs).
XML sitemap (recommended for large-scale websites).
You must use language codes in ISO 639-1 format (e.g., en for English, fr for French). If specifying a region, use ISO 3166-1 Alpha 2 format (e.g., en-US for American English, en-GB for British English).
2. Why is my multilingual website traffic low? I've correctly implemented hreflang.
hreflang only addresses technical indexing and duplicate content issues; it doesn't drive traffic. Low traffic is usually due to:
Failed keyword localization: You directly translated Chinese keywords, which have low search volume in the target market.
Content quality issues: Translated content lacks professionalism and fluency, leading to short user dwell time and high bounce rates.
Lack of localized backlinks: The target language version lacks external links from local authoritative websites, resulting in low authority.
Slow server speed: Slow loading for target users affects user experience and crawling efficiency.
3. How to handle content differences between language versions? Must they be identical?
They shouldn't be identical. While core themes should align, content should adapt to localization needs:
Legal/compliance: Legal information must differ for specific countries.
Products/services: Hide or replace products/services not available in certain countries.
CTAs: Conversion copy and buttons should adapt to local cultural habits. Key: Ensure core functionality and intent remain consistent while correctly declaring relationships in
hreflang.
4. Should I build a multilingual website first or prioritize SEO?
Both should proceed simultaneously. Consider multilingual SEO architecture during website design and development:
Planning: Determine URL structure (subdirectory/subdomain) and CMS multilingual compatibility.
Deployment: Before content launch, plan
hreflangstrategy and conduct localized keyword research.Post-launch: Submit multilingual sitemaps immediately and start building localized backlinks.

Customer Reviews
Mr. Zhang, CEO of a global supply chain solutions company
"Our B2B business requires precise coverage of European and South American markets. Yiyunbao's team built a multilingual website with subdirectory structure and executed extremely meticulous hreflang deployment and localized keyword research. Now, our German and Portuguese websites rank rapidly in local Google searches, delivering high-quality leads and increasing international conversion rates by 30%. Yiyunbao truly transformed our corporate site into a global customer acquisition tool."
Ms. Li, Market Director of a travel tech platform
"We made a major mistake: using simple plugins for automated translation. This left our website almost unranked in overseas search engines. After Yiyunbao's intervention, they first corrected our technical architecture and introduced their AI-assisted translation and professional post-translation editing workflow. Content quality and professionalism improved immediately. Now, our multilingual sites not only gain significant traffic but also achieve double the user dwell time due to excellent localization, with notable improvements in brand trust and booking conversion rates."
![PMax Ads Insider: How Can B2B Enterprises Counterattack to Capture High-Quality Inquiries? PMax Ads Insider: How Can B2B Enterprises Counterattack to Capture High-Quality Inquiries?]() PMax Ads Insider: How Can B2B Enterprises Counterattack to Capture High-Quality Inquiries?PMax Ads Optimization in Action: How Can B2B Enterprises Precisely Capture High-Quality Inquiries?
PMax Ads Insider: How Can B2B Enterprises Counterattack to Capture High-Quality Inquiries?PMax Ads Optimization in Action: How Can B2B Enterprises Precisely Capture High-Quality Inquiries?![2025 Virtual Currency New Era: How Will Application and Technological Innovation Lead the Future Amid Compliant Trends? 2025 Virtual Currency New Era: How Will Application and Technological Innovation Lead the Future Amid Compliant Trends?]() 2025 Virtual Currency New Era: How Will Application and Technological Innovation Lead the Future Amid Compliant Trends?In 2025, How Will Virtual Currency Reshape the Digital Economy? Compliance, Application, and Innovation Advance Together.
2025 Virtual Currency New Era: How Will Application and Technological Innovation Lead the Future Amid Compliant Trends?In 2025, How Will Virtual Currency Reshape the Digital Economy? Compliance, Application, and Innovation Advance Together.![How to Accurately Select Export Trade Professionals? Unveiling the Winning Strategies for Efficient Recruitment! How to Accurately Select Export Trade Professionals? Unveiling the Winning Strategies for Efficient Recruitment!]() How to Accurately Select Export Trade Professionals? Unveiling the Winning Strategies for Efficient Recruitment!Smart Recruitment for Export Sales: Identifying Talents to Build an Elite Team!
How to Accurately Select Export Trade Professionals? Unveiling the Winning Strategies for Efficient Recruitment!Smart Recruitment for Export Sales: Identifying Talents to Build an Elite Team!![EasyBizBoost launches this Wednesday with a 50% speed boost for website loading! A must-see for business owners! EasyBizBoost launches this Wednesday with a 50% speed boost for website loading! A must-see for business owners!]() EasyBizBoost launches this Wednesday with a 50% speed boost for website loading! A must-see for business owners!Urgent call for foreign trade business owners! Solve three major pain points simultaneously: website loading speed/multilingual support/backend efficiency. Capture overseas orders with precision and speed!
EasyBizBoost launches this Wednesday with a 50% speed boost for website loading! A must-see for business owners!Urgent call for foreign trade business owners! Solve three major pain points simultaneously: website loading speed/multilingual support/backend efficiency. Capture overseas orders with precision and speed!![Dare to Send These Gifts in Foreign Trade? Orders Get Canceled Without You Even Knowing! Exposing the Pitfalls 80% of People Stumble Over in Cross-Border Corporate Gifting Dare to Send These Gifts in Foreign Trade? Orders Get Canceled Without You Even Knowing! Exposing the Pitfalls 80% of People Stumble Over in Cross-Border Corporate Gifting]() Dare to Send These Gifts in Foreign Trade? Orders Get Canceled Without You Even Knowing! Exposing the Pitfalls 80% of People Stumble Over in Cross-Border Corporate GiftingHidden Secrets Behind Successful Foreign Trade Orders Lie in Gift Details? Avoid International Etiquette Landmines to Win Client's Hearts!
Dare to Send These Gifts in Foreign Trade? Orders Get Canceled Without You Even Knowing! Exposing the Pitfalls 80% of People Stumble Over in Cross-Border Corporate GiftingHidden Secrets Behind Successful Foreign Trade Orders Lie in Gift Details? Avoid International Etiquette Landmines to Win Client's Hearts!![Are You Losing Money on Facebook Ads? 8 Costly Pitfalls Draining Your Budget! Are You Losing Money on Facebook Ads? 8 Costly Pitfalls Draining Your Budget!]() Are You Losing Money on Facebook Ads? 8 Costly Pitfalls Draining Your Budget!Burning Thousands on Facebook Ads with Few Leads? Avoid These 8 Deadly Traps for Export Business Owners!
Are You Losing Money on Facebook Ads? 8 Costly Pitfalls Draining Your Budget!Burning Thousands on Facebook Ads with Few Leads? Avoid These 8 Deadly Traps for Export Business Owners!![Reverse engineering of OEM products: How does the brand premium magic weave a 300% profit myth? Reverse engineering of OEM products: How does the brand premium magic weave a 300% profit myth?]() Reverse engineering of OEM products: How does the brand premium magic weave a 300% profit myth?Brand premium magic activates OEM potential—the secret weapon for a 300% profit leap is in your hands!
Reverse engineering of OEM products: How does the brand premium magic weave a 300% profit myth?Brand premium magic activates OEM potential—the secret weapon for a 300% profit leap is in your hands!![Losing overseas clients in 3 seconds? Your website might be experiencing a 'digital death countdown'. Losing overseas clients in 3 seconds? Your website might be experiencing a 'digital death countdown'.]() Losing overseas clients in 3 seconds? Your website might be experiencing a 'digital death countdown'.3 seconds to make or break! Is your website losing overseas clients due to language/speed/payment issues? Test now and retain 80% of potential business opportunities!
Losing overseas clients in 3 seconds? Your website might be experiencing a 'digital death countdown'.3 seconds to make or break! Is your website losing overseas clients due to language/speed/payment issues? Test now and retain 80% of potential business opportunities!
![E-Marketing Pro Export Marketing (Super) Website E-Marketing Pro Export Marketing (Super) Website]() E-Marketing Pro Export Marketing (Super) WebsiteE-Yingbao Super Website leverages a robust global server network and CDN acceleration services to ensure lightning-fast access to your site worldwide. This significantly enhances user experience, effectively boosts website loading speeds and retention rates, and empowers your business to achieve global growth.
E-Marketing Pro Export Marketing (Super) WebsiteE-Yingbao Super Website leverages a robust global server network and CDN acceleration services to ensure lightning-fast access to your site worldwide. This significantly enhances user experience, effectively boosts website loading speeds and retention rates, and empowers your business to achieve global growth.![EasyYunbao AI Translation Center EasyYunbao AI Translation Center]() EasyYunbao AI Translation CenterEasyYunbao AI Translation Center: Empowering multilingual standalone websites, enabling seamless global communication. Integrates Google Neural Machine Translation technology to generate multilingual websites with one click, achieving intelligent localization for foreign trade standalone sites and enhancing global market competitiveness.
EasyYunbao AI Translation CenterEasyYunbao AI Translation Center: Empowering multilingual standalone websites, enabling seamless global communication. Integrates Google Neural Machine Translation technology to generate multilingual websites with one click, achieving intelligent localization for foreign trade standalone sites and enhancing global market competitiveness.![Multilingual Website Solutions for Foreign Trade Multilingual Website Solutions for Foreign Trade]() Multilingual Website Solutions for Foreign TradeE-Yingbao SAAS Smart Website Builder offers precise translations in over 300 minor languages, overcoming language barriers for export businesses and boosting order conversion rates. Supporting all devices, global languages, SEO optimization, and omnichannel promotion, it empowers you to effortlessly expand into international markets.
Multilingual Website Solutions for Foreign TradeE-Yingbao SAAS Smart Website Builder offers precise translations in over 300 minor languages, overcoming language barriers for export businesses and boosting order conversion rates. Supporting all devices, global languages, SEO optimization, and omnichannel promotion, it empowers you to effortlessly expand into international markets.![Global CDN Acceleration for B2B Foreign Trade Website Building Global CDN Acceleration for B2B Foreign Trade Website Building]() Global CDN Acceleration for B2B Foreign Trade Website BuildingAgainst the backdrop of digital transformation in global trade, foreign trade enterprises face the dual challenges of cross-border network latency and geographical information search (GEO) disparities. The 'Global CDN Acceleration for B2B Foreign Trade Website Building' solution introduced by EasyCamp not only enhances webpage loading speed but also integrates search engine optimization (SEO) with GEO as a systematic engineering approach. By establishing multiple edge nodes worldwide, it ensures that overseas buyers can instantly access corporate websites regardless of their location, significantly improving brand first impressions and inquiry conversion rates.
Global CDN Acceleration for B2B Foreign Trade Website BuildingAgainst the backdrop of digital transformation in global trade, foreign trade enterprises face the dual challenges of cross-border network latency and geographical information search (GEO) disparities. The 'Global CDN Acceleration for B2B Foreign Trade Website Building' solution introduced by EasyCamp not only enhances webpage loading speed but also integrates search engine optimization (SEO) with GEO as a systematic engineering approach. By establishing multiple edge nodes worldwide, it ensures that overseas buyers can instantly access corporate websites regardless of their location, significantly improving brand first impressions and inquiry conversion rates.