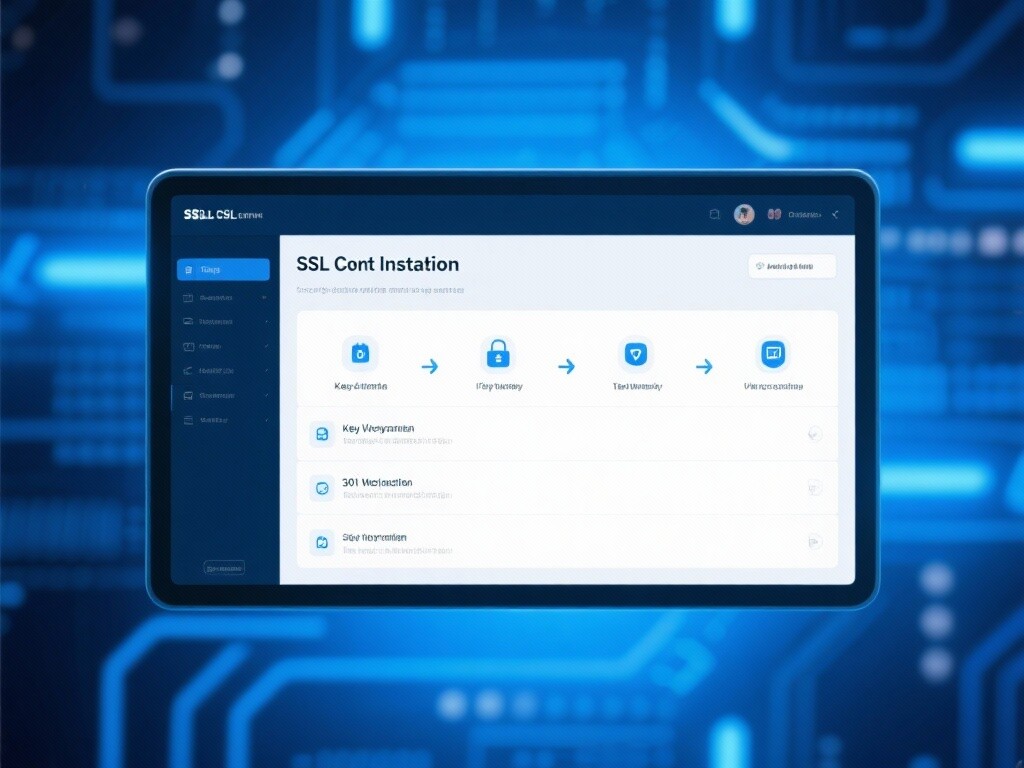
I. Authoritative Definition and Core Value of SSL Certificate Installation
1. Authoritative Definition of SSL Certificate Installation
SSL Certificate Installation refers to the process of deploying a digital certificate (SSL/TLS Certificate) on a website server (such as Apache, Nginx, IIS, etc.) and configuring the server to enable the HTTPS (Hypertext Transfer Protocol Secure) encrypted connection protocol.
Core Functionality: Through the SSL/TLS protocol, an encrypted channel is established between the user's browser and the website server, ensuring the confidentiality, integrity, and identity authentication of data transmission.
Final Outcome: The website URL changes from http:// to https://, and a security lock icon is displayed in the browser address bar.
2. Strategic Core Value of SSL Certificate Installation: $4$ Major SEO and Business Drivers
II. Development History of SSL Certificates and Evolution of Security Protocols
The development history of SSL/TLS protocols is an evolutionary journey from basic encryption to high-strength security, from optional features to mandatory standards.
1. Early Stage: SSL$1.0 / 2.0$ and the Rise of E-Commerce (1990s-2000s)
Technical Focus:Netscape pioneered the development of the SSL protocol. It was primarily used for early e-commerce websites and payment pages.
Security Flaws: Early protocols had design defects and vulnerabilities, with low encryption strength.
Market Position: SSL certificates were viewed as a premium, high-end additional feature.
2. Mid-Stage: TLS Upgrade and Internet Popularization (2000s-2014)
Milestone:TLS (Transport Layer Security) protocol replaced SSL (though we still commonly refer to it as SSL certificates). TLS $1.0$, $1.1$, and $1.2$ were successively released.
Strategic Shift:Services like email and online banking began widely adopting SSL/TLS.
SEO Impact:Google had not yet listed HTTPS as a ranking factor, and most websites still used HTTP.
3. Modern Stage: TLS $1.3$, Google Enforcement, and "Security First" (2014 to Present)
Core Focus:Internet security and privacy protection became mandatory standards.
Strategic Deepening:
In 2014, Google officially announced HTTPS as a ranking signal, ushering in the era of "Full-Site HTTPS".
In 2017, Chrome began labeling all HTTP websites as "Not Secure".
TLS $1.3$ Release:Further simplified the protocol, improved encryption strength, and connection speed.
Let's Encrypt Popularization:The emergence of free SSL certificates significantly lowered the installation barrier.
Trend: Modern SSL certificate installation is a foundational technical standard for website construction, with $0$ tolerance.
III. Technical Principles of SSL Certificate Installation: $4$ Key Steps and Key Exchange
SSL certificates enable encrypted communication, relying on **Public Key Infrastructure (PKI) and the complex encryption handshake (Handshake)** process between the browser and server.
1. Certificate Verification and Identity Authentication (Authentication)
Principle: When the browser initiates a connection request to the server, the server sends its SSL certificate. The certificate contains the server's public key and the digital signature of the Certificate Authority (CA).
Technical Process: The browser uses the built-in CA root certificate public key to verify the signature on the server certificate. If the signature is valid, it proves the server's identity is trustworthy.
2. Encryption Handshake and Key Exchange (Key Exchange)
Principle: Both parties need to negotiate a temporary, symmetric session key for encrypting subsequent data transmissions.
Technical Process:
The browser generates a random "pre-master key".
The browser encrypts this pre-master key using the server's public key (from the certificate).
After receiving the encrypted pre-master key, the server uses its private key to decrypt it, thereby obtaining the symmetric session key. The private key is the only means of decryption, making $100%$ secrecy the cornerstone of security.
3. Symmetric Encrypted Communication (Encrypted Communication)
Principle:After a successful handshake, both parties obtain the same session key.
Technical Process:All subsequent data transmissions use this symmetric key for efficient encryption and decryption. Symmetric encryption is faster than asymmetric encryption, ensuring website performance.
4. $301$ Redirect and Full-Site $HTTPS$ Deployment (Redirection)
Principle:Ensure $100%$ of HTTP traffic is permanently redirected to HTTPS addresses.
Technical Implementation:Set a $301$ permanent redirect rule in the server configuration file (e.g.,
.htaccessor Nginx Conf). This is the critical step after SSL certificate installation to achieve SEO weight transfer and full-site security coverage.
IV. $5$ Major Types of SSL Certificates and Selection Guide
Professional SSL certificate installation services will select the most suitable certificate type based on the client's security requirements, application scenarios, and budget.
V. $6$ Core Technical Steps and Applications of SSL Certificate Installation
Professional SSL certificate installation services not only install certificates but also perform comprehensive security configurations and SEO optimizations.

1.Certificate Generation and Server Preparation (CSR Generation)
Technical Key Points: On the server, generate a Certificate Signing Request (CSR), which includes a unique public and private key. The private key must $100%$ be securely stored on the server.
2. Certificate Installation and Configuration (Installation)
Technical Key Points:Upload the certificate file (CRT) issued by the CA to the server, and specify the certificate file path, private key file path, and intermediate certificate (CA Bundle) in the server configuration file.
3. Full-Site $301$ Redirect Configuration (SEO Compliance)
Technical Key Points:Set a $301$ permanent redirect in the Nginx/Apache configuration file, redirecting all
http://traffic tohttps://. This is the critical step to achieve lossless SEO weight transfer.
4. Mixed Content Repair
Technical Key Points:Scan all website pages to find resources still loaded via HTTP protocol (such as images, $CSS$, $JS$). Systematically correct their URLs to HTTPS protocol or relative paths. Mixed content is the main cause of "Not Secure" warnings and SEO ranking penalties.
5. HSTS Security Header Configuration (Advanced Security)
Technical Key Points:Add HSTS (HTTP Strict Transport Security) to the server response header. Force browsers to use only HTTPS for access within $1 text{ year}$ or longer, effectively preventing SSL stripping attacks.
6. GSC and Baidu Webmaster Platform Updates
Technical Key Points:After SSL certificate installation, it is essential to add the new HTTPS version in Google Search Console and Baidu Webmaster Platform, and perform site verification and $Sitemap$ updates, notifying search engines for rapid indexing and weight transfer.
VI. Easy Treasure: Your SSL Certificate Installation and Security Optimization Expert
Easy Treasure specializes in providing one-stop, efficient, high-security standard SSL certificate installation solutions. We don’t just provide certificates; more importantly, we offer full-site $HTTPS$ configuration, $301$ redirect optimization, and deep mixed content repair, ensuring your website is compliant, secure, and maximizes SEO ranking benefits.
Get Free SSL Certificate Type Recommendations Immediately
** Complete SSL Certificate Installation and Full-Site $HTTPS$ Deployment Within $24 text{ hours}$**
**$100%$ Elimination of "Not Secure" Warnings, Ensuring Lossless SEO Weight Transfer**
Build Secure, Professional, High-Conversion Digital Assets with Easy Treasure!
FAQ
1. Why does my website still show "Not Secure" after installing an SSL certificate?
Answer: This is usually caused by "Mixed Content" issues.
Reason: Although your homepage loads via HTTPS, some resources (e.g., images, $CSS$ files, $JS$ scripts) still load via insecure HTTP.
Solution: Use professional tools to scan the website, locate all HTTP resources, and force their URLs to HTTPS or use relative paths. This is a meticulous and critical SEO technical step.
2. Is HTTPS a Google ranking factor? How much does it impact SEO weight?
Answer: Yes, HTTPS is officially announced by Google as a "lightweight" ranking factor, but its indirect impact is enormous.
Direct impact: HTTPS itself provides a ranking boost, though not decisive, secure websites gain ranking advantages under equal conditions.
Indirect impact: Secure websites reduce bounce rates and enhance user trust, which significantly affects SEO weight. Most importantly, without HTTPS, your website will face browser warnings, leading to plummeting traffic and conversions.
3. What’s the difference between free SSL certificates (e.g., Let's Encrypt) and paid certificates (e.g., OV/EV)? Which should I choose?
Answer: Main differences lie in "validation levels" and "trust levels".
Free certificates (DV): Only verify domain ownership. Suitable for personal blogs and small info sites. Lowest trust level, requires manual renewal every $3$ months.
Paid certificates (OV/EV): Verify company/organization authenticity. EV certificates display the company name in green in the address bar, offering the highest trust level. Ideal for e-commerce, finance, and high-value B2B enterprises, directly boosting brand professionalism and conversion rates.
4. After installing an SSL certificate, do I need to set up $301$ redirects? How does this impact SEO?
Answer: ** $100%$ need to set up $301$ redirects—this is the most crucial SEO step after SSL installation.**
Reason: Search engines treat
http://andhttps://as two different websites. Without $301$ permanent redirects, you’ll face severe SEO issues like split authority and duplicate content.Effect: ** $301$ redirects transfer $90%+$ of the old HTTP authority losslessly to the new HTTPS address**, ensuring your website’s traffic and rankings remain unaffected by the migration.

Customer Reviews
Mr. Sun, CMO of a Global B2B Industrial Tech Company
"Our previous foreign trade website lacked an SSL certificate and often received customer feedback about 'Not Secure' warnings. EasySSL’s SSL certificate installation service not only deployed an OV-level certificate for us, more importantly, they professionally completed full-site $301$ redirects and mixed content fixes. After smoothly migrating to HTTPS, we saw a significant improvement in security ratings in Google Search Console, with core keyword rankings rising by an average of $3$ positions. Security truly became our competitive edge."
Ms. Qi, CEO of a Large DTC Cross-Border E-Commerce Company
"For e-commerce, payment security is a lifeline. The EasySSL team selected an EV Extended Validation SSL certificate for us, and completed installation and HSTS configuration within $24 text{ hours}$. The security lock icon and green company name greatly enhanced customer trust, while their seamless $301$ migration ensured our traffic stability. Now, we are $100%$ confident our website meets the highest global security and SEO standards."
![Can AI+SEO Dual Engine Optimization System Really Improve Rankings? 3 Months of Actual Data Tells the Story Can AI+SEO Dual Engine Optimization System Really Improve Rankings? 3 Months of Actual Data Tells the Story]() Can AI+SEO Dual Engine Optimization System Really Improve Rankings? 3 Months of Actual Data Tells the StoryAI+SEO Dual Engine Optimization System Really Improves Rankings? 3 Months of Data Shows a 340% Increase in Organic Traffic for B2B Export Websites with AI+SEM Smart Advertising and Global CDN Acceleration. Through Multilingual Independent Site Construction, SSL Certificate Installation, and Localization Optimization, Google Rankings and Conversion Efficiency Are Significantly Enhanced. In Testing, Core Keywords Jumped from #67 to #6, with a 210% Increase in Ad Click-Through Rates in the Russian Market. The System Also Supports City Partner Ecosystems and EasyTreasure Agency Policies, Empowering Entrepreneurs to Share AI Marketing Dividends. From Technical Architecture to Marketing Implementation, Covering Website Building, Security, SEO, and Full-Path Advertising, Truly Enabling Intelligent Global Expansion. Learn How AI Tools Reduce Customer Acquisition Costs and Seize Global Market Opportunities Now.
Can AI+SEO Dual Engine Optimization System Really Improve Rankings? 3 Months of Actual Data Tells the StoryAI+SEO Dual Engine Optimization System Really Improves Rankings? 3 Months of Data Shows a 340% Increase in Organic Traffic for B2B Export Websites with AI+SEM Smart Advertising and Global CDN Acceleration. Through Multilingual Independent Site Construction, SSL Certificate Installation, and Localization Optimization, Google Rankings and Conversion Efficiency Are Significantly Enhanced. In Testing, Core Keywords Jumped from #67 to #6, with a 210% Increase in Ad Click-Through Rates in the Russian Market. The System Also Supports City Partner Ecosystems and EasyTreasure Agency Policies, Empowering Entrepreneurs to Share AI Marketing Dividends. From Technical Architecture to Marketing Implementation, Covering Website Building, Security, SEO, and Full-Path Advertising, Truly Enabling Intelligent Global Expansion. Learn How AI Tools Reduce Customer Acquisition Costs and Seize Global Market Opportunities Now.![Does LinkedIn's automated marketing strategy comply with GDPR? 5 essential user authorization and log retention settings that EU distributors must check. Does LinkedIn's automated marketing strategy comply with GDPR? 5 essential user authorization and log retention settings that EU distributors must check.]() Does LinkedIn's automated marketing strategy comply with GDPR? 5 essential user authorization and log retention settings that EU distributors must check.Is LinkedIn's automated marketing strategy compliant? 5 essential GDPR settings EU distributors must check: User authorization, log retention, SSL certificate security configuration, AI marketing engine SEO optimization, and multi-language support for social media automation!
Does LinkedIn's automated marketing strategy comply with GDPR? 5 essential user authorization and log retention settings that EU distributors must check.Is LinkedIn's automated marketing strategy compliant? 5 essential GDPR settings EU distributors must check: User authorization, log retention, SSL certificate security configuration, AI marketing engine SEO optimization, and multi-language support for social media automation!![Global CDN Acceleration vs Local Servers: How Big Is the Actual Loading Speed Difference? Global CDN Acceleration vs Local Servers: How Big Is the Actual Loading Speed Difference?]() Global CDN Acceleration vs Local Servers: How Big Is the Actual Loading Speed Difference?How Does Global CDN Acceleration Outperform Local Servers? Actual Tests Show a 68.4% Improvement in Loading Speed, with First Screen Time Reduced from 3.8 Seconds to 1.2 Seconds, Significantly Lowering Bounce Rates. EasyStore, an All-in-One Marketing Platform, Integrates Global CDN Acceleration, AI+SEO Dual-Engine Optimization System, and AI+SEM Smart Ad Marketing System, Supporting Multilingual Foreign Trade Independent Site Construction with Automatic SSL Certificate Installation for Security Compliance. Empowering B2B Foreign Trade Websites for Efficient Global Expansion, Now Open for City Partner Recruitment and EasyStore Agent Alliance Policies. Click to Learn About Technical Advantages and Partnership Opportunities.
Global CDN Acceleration vs Local Servers: How Big Is the Actual Loading Speed Difference?How Does Global CDN Acceleration Outperform Local Servers? Actual Tests Show a 68.4% Improvement in Loading Speed, with First Screen Time Reduced from 3.8 Seconds to 1.2 Seconds, Significantly Lowering Bounce Rates. EasyStore, an All-in-One Marketing Platform, Integrates Global CDN Acceleration, AI+SEO Dual-Engine Optimization System, and AI+SEM Smart Ad Marketing System, Supporting Multilingual Foreign Trade Independent Site Construction with Automatic SSL Certificate Installation for Security Compliance. Empowering B2B Foreign Trade Websites for Efficient Global Expansion, Now Open for City Partner Recruitment and EasyStore Agent Alliance Policies. Click to Learn About Technical Advantages and Partnership Opportunities.![Global CDN acceleration results in higher latency? These configuration pitfalls you might have stepped into Global CDN acceleration results in higher latency? These configuration pitfalls you might have stepped into]() Global CDN acceleration results in higher latency? These configuration pitfalls you might have stepped intoGlobal CDN acceleration latency increased? It might be caused by improper SSL certificate installation or configuration. Easy Marketing, an all-in-one marketing platform, integrates AI+SEO dual-engine optimization systems and AI+SEM intelligent ad marketing systems, empowering B2B foreign trade website construction and multilingual independent site building. It intelligently schedules over 200 global nodes, automatically completes SSL certificate installation, and enhances loading speed and SEO rankings. Now open for city partner recruitment and Easy Marketing agent alliance policies, empowering enterprises to expand overseas efficiently. Click to learn about B2B2C dual-model independent site solutions, achieving traffic and conversion dual growth.
Global CDN acceleration results in higher latency? These configuration pitfalls you might have stepped intoGlobal CDN acceleration latency increased? It might be caused by improper SSL certificate installation or configuration. Easy Marketing, an all-in-one marketing platform, integrates AI+SEO dual-engine optimization systems and AI+SEM intelligent ad marketing systems, empowering B2B foreign trade website construction and multilingual independent site building. It intelligently schedules over 200 global nodes, automatically completes SSL certificate installation, and enhances loading speed and SEO rankings. Now open for city partner recruitment and Easy Marketing agent alliance policies, empowering enterprises to expand overseas efficiently. Click to learn about B2B2C dual-model independent site solutions, achieving traffic and conversion dual growth.![Is the cost of building a B2B foreign trade website too high? 3 low-cost high-conversion solutions revealed Is the cost of building a B2B foreign trade website too high? 3 low-cost high-conversion solutions revealed]() Is the cost of building a B2B foreign trade website too high? 3 low-cost high-conversion solutions revealedIs the cost of building a B2B foreign trade website high? EasyStore launches an AI+SEO dual-engine optimization system to help enterprises create multilingual foreign trade independent websites at low cost. Integrated all-in-one marketing platform, global CDN acceleration and automatic SSL certificate installation, website construction cycle shortened to 3-7 days, annual operation and maintenance costs reduced by over 60%. Equipped with AI+SEM smart advertising system, conversion rate increased by 200%. Now open for city partner recruitment and agent joining policy, empowering regional service providers to share AI dividends. Build a high-conversion independent website with one click, opening a new chapter in intelligent overseas expansion!
Is the cost of building a B2B foreign trade website too high? 3 low-cost high-conversion solutions revealedIs the cost of building a B2B foreign trade website high? EasyStore launches an AI+SEO dual-engine optimization system to help enterprises create multilingual foreign trade independent websites at low cost. Integrated all-in-one marketing platform, global CDN acceleration and automatic SSL certificate installation, website construction cycle shortened to 3-7 days, annual operation and maintenance costs reduced by over 60%. Equipped with AI+SEM smart advertising system, conversion rate increased by 200%. Now open for city partner recruitment and agent joining policy, empowering regional service providers to share AI dividends. Build a high-conversion independent website with one click, opening a new chapter in intelligent overseas expansion!![SSL Certificate Installation Always Failing? 3 Steps to Solve Common Errors SSL Certificate Installation Always Failing? 3 Steps to Solve Common Errors]() SSL Certificate Installation Always Failing? 3 Steps to Solve Common ErrorsSSL Certificate Installation Failed? 3-Step Troubleshooting to Quickly Resolve Configuration Issues, Ensuring Security and Stability for B2B Foreign Trade Websites. YeeSpot Offers an All-in-One Marketing Platform, Supporting Multilingual Foreign Trade Independent Site Building, Global CDN Acceleration, and AI+SEO Dual-Engine Optimization System, with Built-in Automatic SSL Deployment and AI+SEM Smart Ad Marketing System. From Local City Partner Support to Agent Alliance Policies, We Provide Full Journey Protection for Businesses Going Global, Helping with Efficient Customer Acquisition and Security Compliance.
SSL Certificate Installation Always Failing? 3 Steps to Solve Common ErrorsSSL Certificate Installation Failed? 3-Step Troubleshooting to Quickly Resolve Configuration Issues, Ensuring Security and Stability for B2B Foreign Trade Websites. YeeSpot Offers an All-in-One Marketing Platform, Supporting Multilingual Foreign Trade Independent Site Building, Global CDN Acceleration, and AI+SEO Dual-Engine Optimization System, with Built-in Automatic SSL Deployment and AI+SEM Smart Ad Marketing System. From Local City Partner Support to Agent Alliance Policies, We Provide Full Journey Protection for Businesses Going Global, Helping with Efficient Customer Acquisition and Security Compliance.![How long does it take to build a multilingual foreign trade independent website? The fastest way to go live in 24 hours How long does it take to build a multilingual foreign trade independent website? The fastest way to go live in 24 hours]() How long does it take to build a multilingual foreign trade independent website? The fastest way to go live in 24 hoursHow to launch a multilingual foreign trade independent website in just 24 hours? EasyStore AI+SEO dual-engine optimization system integrates global CDN acceleration and SSL certificate installation to help businesses build websites efficiently. Supports one-click multilingual adaptation, AI intelligent translation, and AI+SEM smart advertising marketing system, comprehensively enhancing overseas lead generation capabilities. Learn about the City Partner Program and EasyStore's agent alliance policy to share the benefits of an all-in-one marketing platform, empowering a new paradigm for B2B foreign trade website building. Get your exclusive solution now and embark on China's intelligent brand globalization journey.
How long does it take to build a multilingual foreign trade independent website? The fastest way to go live in 24 hoursHow to launch a multilingual foreign trade independent website in just 24 hours? EasyStore AI+SEO dual-engine optimization system integrates global CDN acceleration and SSL certificate installation to help businesses build websites efficiently. Supports one-click multilingual adaptation, AI intelligent translation, and AI+SEM smart advertising marketing system, comprehensively enhancing overseas lead generation capabilities. Learn about the City Partner Program and EasyStore's agent alliance policy to share the benefits of an all-in-one marketing platform, empowering a new paradigm for B2B foreign trade website building. Get your exclusive solution now and embark on China's intelligent brand globalization journey.![Is an all-in-one marketing platform worth it? After comparing 5 major tools, I chose this one Is an all-in-one marketing platform worth it? After comparing 5 major tools, I chose this one]() Is an all-in-one marketing platform worth it? After comparing 5 major tools, I chose this oneAfter evaluating 5 mainstream tools, I opted for EasyYun's all-in-one marketing platform — integrating an AI+SEO dual-engine optimization system, AI+SEM intelligent ad marketing system, global CDN acceleration, and multilingual foreign trade independent site construction into one solution. It helps enterprises efficiently build websites and implement smart promotions. Supports automatic SSL certificate installation to ensure data security and compliance, especially suitable for B2B foreign trade website needs. Leveraging the city partner model and EasyYun's agency alliance policy, it has served over 30 provinces nationwide, providing end-to-end solutions from website construction to customer acquisition for export-oriented enterprises. Learn now how to achieve precise投放 through AI technology, improve conversion rates, and seize opportunities in overseas markets.
Is an all-in-one marketing platform worth it? After comparing 5 major tools, I chose this oneAfter evaluating 5 mainstream tools, I opted for EasyYun's all-in-one marketing platform — integrating an AI+SEO dual-engine optimization system, AI+SEM intelligent ad marketing system, global CDN acceleration, and multilingual foreign trade independent site construction into one solution. It helps enterprises efficiently build websites and implement smart promotions. Supports automatic SSL certificate installation to ensure data security and compliance, especially suitable for B2B foreign trade website needs. Leveraging the city partner model and EasyYun's agency alliance policy, it has served over 30 provinces nationwide, providing end-to-end solutions from website construction to customer acquisition for export-oriented enterprises. Learn now how to achieve precise投放 through AI technology, improve conversion rates, and seize opportunities in overseas markets.