I. Authoritative Definition, Key Challenges, and Development History of Multilingual SEO Optimization
1. Authoritative Definition of Multilingual SEO Optimization
Multilingual SEO (Multilingual SEO) refers to a series of **technical and content optimization measures** adopted for websites with multiple language versions to ensure that search engines (especially Google) can **correctly identify, crawl, and index** content in different language versions and accurately recommend it to search users in the corresponding language and region. Its core goal is to **avoid duplicate content penalties** and achieve **accurate geographic targeting (Geo-targeting)**.
2. Three Key Challenges of Multilingual SEO
Foreign trade enterprises often face the following challenges when implementing multilingual SEO:
- **Duplicate Content Issues:** Simple translations may be considered duplicate content by Google, leading to ranking losses for all versions.
- **Hreflang Deployment Errors:** The tag syntax is complex, and any minor error may result in failed geographic targeting and traffic confusion.
- **Insufficient Content Localization:** Although content is translated, it may not incorporate local culture, search habits, or product terminology, resulting in extremely low conversion rates.
3. Development History of Multilingual SEO
Early Stage (2000s): Primarily relied on **independent country-code top-level domains (ccTLD)** for geographic targeting. Mid-Stage (2011): Google introduced **Hreflang tags**, providing a more flexible solution for language and region targeting. Modern Era (2020s to Present): Multilingual SEO trends toward **technical automation (Hreflang auto-maintenance)** and **content intent localization**, combined with **global CDN** to solve cross-border access speed issues.

II. Five Core Technical Principles of Multilingual SEO Optimization: Hreflang and Architecture
The success of multilingual SEO depends on precise execution of Google's internationalization rules:
1. Hreflang Tag Mechanism Principle
Principle: Hreflang is an HTML attribute used to inform search engines that **a page has versions in other languages or regions**. Technical Application: It uses the `link rel="alternate" hreflang="xx-XX"` format, where `xx` is the language code and `XX` is the region code. All interlinked pages must form a **bidirectional closed loop**; otherwise, Google will ignore the tag. This is the official solution for multilingual duplicate content issues.
2. Multilingual URL Architecture Selection Principle
Principle: The website's structural division affects Google's **geographic attribution judgment** and **authority distribution**. Technical Application: There are three main structures: **Subdirectory** (`example.com/fr/`, centralized authority, suitable for unified branding); **Subdomain** (`fr.example.com`, convenient for CDN configuration); **Independent Domain** (`example.fr`, strongest geographic signal but highest operational cost). The choice should be based on the brand's global strategy and SEO needs.
3. Geo-targeting Principle
Principle: Inform Google of the target user group's region. Technical Application: Besides Hreflang, **Google Search Console's international targeting settings, ccTLD (country-code top-level domains), and server IP addresses** are also important geographic signals. Professional SEO must ensure all signals are **consistent and clear**, avoiding conflicts.
4. Content Localization and Search Intent Matching Principle
Principle: High-quality multilingual content must reflect local users' search habits and cultural preferences. Technical Application: Localization goes beyond **language translation** and includes **currency, date formats, measurement units, and target keyword selection**. For example, Spanish expressions vary significantly between Spain and Mexico, requiring targeted optimization.
5. Global CDN and Cross-Border Performance Principle
Principle: Solve international visitor latency issues and ensure Core Web Vitals (CWV) compliance. Technical Application: Deploy **Global Content Delivery Network (CDN)** to cache website resources on edge servers close to users. This is especially critical for multilingual websites, significantly improving loading speeds and user experience across different countries/regions.
III. Four Core Technical Features and Applications of Multilingual SEO Optimization
1. Technical Feature: Best Practices for Language Switchers
Feature: User-friendly language switching mechanisms. Application: Professional practice involves **avoiding country flag icons** (due to multilingual countries or multi-country languages) and using clear **language names (e.g., Spanish, Deutsch)**. Language switchers should serve as **pure UX aids** and not replace the technical directives of Hreflang.
2. Application Practice: Multilingual Keyword Research for Foreign Trade Products
Application: Foreign trade enterprises must research **localized keywords** for target markets. For example, an industrial product may use a technical term in Germany but a synonymous term in France. Multilingual SEO optimization requires **independent keyword research and content mapping** for **each target language version**.
3. Application Practice: Multilingual Link Building Strategies
Application: Link building should follow multilingual principles. Efforts should be made to acquire **backlinks from target country/region websites**. For example, for a German version website, prioritize high-authority backlinks from Germany or German-speaking regions, significantly enhancing Google's geographic attribution signal for the German version.
4. Application Practice: Strategies for Handling "Untranslated Content"
Application: For niche markets where enterprises may not fully translate all content, the best practice is to use **X-default Hreflang tags** to specify a **default or primary version** page for users not matching any defined language or region. Additionally, **avoid machine translation tools** (e.g., Google Translate Widget), as they can damage the SEO value of content.
IV. Comparative Analysis and Industry Application Scenarios of Multilingual SEO Optimization

1. Comparative Analysis of Multilingual Architectures: Subdirectory vs. Subdomain vs. Independent Domain
2. Typical Industry Application Scenarios of Multilingual SEO Optimization
Multilingual SEO plays a key role in different industries:
- **B2B Industrial Manufacturing:** Adopt **subdirectory architecture**, focusing on consolidating brand authority under the main domain. Prioritize deep localization and Hreflang deployment for **high-value query markets** like German, Spanish, and French.
- **Cross-Border B2C E-commerce Platforms:** Use **subdomain architecture** for independent handling of **currency, taxes, and payment systems** across different countries/regions, achieving precise product and pricing positioning through Geo-targeting.
- **Service-Oriented Export Enterprises (e.g., Consulting):** Use **independent domains** for core target markets (e.g., `example.jp`) to establish **absolute local trust and authority**, despite higher costs, for significant results.
3. Certification and Compliance of Multilingual SEO
Professional globalized SEO must adhere to the following standards:
- **Hreflang Validation:** Use **Google Search Console** to regularly check for Hreflang tag errors and conflicts.
- **CWV International Standards:** Ensure the website meets Google's CWV requirements in different target countries.
- **Internationalization Tools:** Proficiently use tools like **Ahrefs and Semrush** for multilingual keyword ranking monitoring and competitor analysis.
V. Embrace Multilingual SEO Optimization Now and Unlock Overlooked Global Traffic!
Is your multilingual website losing global traffic due to Hreflang deployment errors or insufficient content localization? Don't let technical barriers limit your international growth! Let experienced foreign trade SEO experts customize a **multilingual SEO optimization strategy** covering **architecture selection, Hreflang automation, content intent localization, and global performance optimization**. Book a **free "Multilingual Website Internationalization Diagnostic"** now to receive a professional Hreflang deployment and global traffic growth plan, making your brand a true global authority!
Click to Get a Free Multilingual SEO Diagnostic ReportFAQ
1. What is an Hreflang tag, and how is it different from translation?
Answer: The Hreflang tag is a technical signal used to inform Google about the 'language' and 'region' versions of a page, thereby avoiding duplicate content issues and achieving geographic targeting. It is unrelated to the translated content itself but ensures that translated content can be correctly indexed through key technical steps.
2. Should I choose a subdirectory or subdomain for multilingual website architecture?
Answer: For most foreign trade enterprises, **subdirectories (example.com/fr/)** are the preferred choice. They consolidate the SEO authority of all language versions under the main domain, with lower operational costs and better authority accumulation. Subdomains are suitable for large multinational companies requiring independent hosting, independent branding, or independent Geo-targeting.
3. Can machine-translated content be used for multilingual SEO optimization?
Answer: **Pure machine-translated content absolutely cannot be used for SEO.** Google's algorithms can identify low-quality machine translations and may penalize rankings. Multilingual SEO emphasizes **content localization**, requiring **professional human translation, cultural adaptation, and keyword optimization** to match local search intent.
4. How to handle 'untranslated' pages in a multilingual website?
Answer: For untranslated pages, use the **'x-default' tag** in the Hreflang set. `x-default` specifies a default or universal version for search users not matching any defined language or region, a crucial compliance measure for internationalized SEO.

Customer Reviews
Mr. Li, CEO of Asian High-Tech Equipment Exporter
"Our traffic in Europe has always been very chaotic, and rankings never improved. After diagnosis by a professional team, we found major errors in Hreflang implementation. They helped us adopt an **integrated SaaS platform** for automated Hreflang maintenance and **multilingual content localization**. **Now our German and French versions have achieved 85% traffic growth, with significantly improved inquiry quality.** Multilingual SEO optimization is indeed a technical game-changer."
Manager Chen, North America B2C Cross-Border E-Commerce
"We chose a **subdomain architecture** for multilingual optimization. The professional team not only solved technical issues but also implemented **global CDN deployment**, achieving Google CWV's excellent standards for loading speeds in the US, UK, and Australia. **The dual improvement in user experience and SEO performance drove our multi-market sales to grow over 50% within one year.**"
![Unveiling the Goldmine in Niche Markets: Why Does Your Independent Site Need to 'Speak Dialects'? Unveiling the Goldmine in Niche Markets: Why Does Your Independent Site Need to 'Speak Dialects'?]() Unveiling the Goldmine in Niche Markets: Why Does Your Independent Site Need to 'Speak Dialects'?Amid global fragmentation, niche markets with languages like Russian and Arabic are unlocking trillion-level opportunities. How can export-oriented businesses break through language barriers with independent sites? Easy-Commerce AI Translation Engine leverages local language adaptation technology to redefine cross-border lead acquisition.
Unveiling the Goldmine in Niche Markets: Why Does Your Independent Site Need to 'Speak Dialects'?Amid global fragmentation, niche markets with languages like Russian and Arabic are unlocking trillion-level opportunities. How can export-oriented businesses break through language barriers with independent sites? Easy-Commerce AI Translation Engine leverages local language adaptation technology to redefine cross-border lead acquisition.![Dalian multilingual website construction, how to improve user experience? Dalian multilingual website construction, how to improve user experience?]() Dalian multilingual website construction, how to improve user experience?This article discusses in detail how Dalian's multilingual website construction can improve user experience, covering multilingual website design principles, technical implementation solutions and optimization strategies. It is suitable for multilingual website construction projects of enterprises in Dongguan, Foshan, Zhongshan, Huizhou, Zhengzhou, Shenzhen, Guangzhou, Beijing and other places.
Dalian multilingual website construction, how to improve user experience?This article discusses in detail how Dalian's multilingual website construction can improve user experience, covering multilingual website design principles, technical implementation solutions and optimization strategies. It is suitable for multilingual website construction projects of enterprises in Dongguan, Foshan, Zhongshan, Huizhou, Zhengzhou, Shenzhen, Guangzhou, Beijing and other places.![Huizhou Multilingual Website Development: Essential for Corporate Globalization Huizhou Multilingual Website Development: Essential for Corporate Globalization]() Huizhou Multilingual Website Development: Essential for Corporate GlobalizationThis article provides an in-depth analysis of the importance of Huizhou multilingual website development for corporate globalization, comparing the characteristics of website production in Dongguan, Foshan, Zhongshan, Dalian, Zhengzhou, Shenzhen, Guangzhou, Beijing, and other regions. It offers professional website development recommendations and global marketing strategies to help businesses overcome language barriers and expand into international markets.
Huizhou Multilingual Website Development: Essential for Corporate GlobalizationThis article provides an in-depth analysis of the importance of Huizhou multilingual website development for corporate globalization, comparing the characteristics of website production in Dongguan, Foshan, Zhongshan, Dalian, Zhengzhou, Shenzhen, Guangzhou, Beijing, and other regions. It offers professional website development recommendations and global marketing strategies to help businesses overcome language barriers and expand into international markets.![How to choose the right multilingual website development solution for Zhongshan? How to choose the right multilingual website development solution for Zhongshan?]() How to choose the right multilingual website development solution for Zhongshan?This article provides an in-depth analysis of key factors in Zhongshan multilingual website development, comparing the advantages of different solutions to offer professional recommendations. Covering website construction needs in Dongguan, Foshan, Huizhou, Dalian, Zhengzhou, Shenzhen, Guangzhou, Beijing and other regions, helping businesses find the most suitable solution.
How to choose the right multilingual website development solution for Zhongshan?This article provides an in-depth analysis of key factors in Zhongshan multilingual website development, comparing the advantages of different solutions to offer professional recommendations. Covering website construction needs in Dongguan, Foshan, Huizhou, Dalian, Zhengzhou, Shenzhen, Guangzhou, Beijing and other regions, helping businesses find the most suitable solution.![Detailed explanation of the service process of Foshan multilingual website production company Detailed explanation of the service process of Foshan multilingual website production company]() Detailed explanation of the service process of Foshan multilingual website production companyThis article analyzes in detail the professional service process of Foshan multilingual website production company, covering key links such as demand analysis, multilingual adaptation, UI design, program development, etc., and compares the service differences in Dongguan, Zhongshan, Huizhou and other regions, providing a practical guide for enterprises to choose multilingual website construction services.
Detailed explanation of the service process of Foshan multilingual website production companyThis article analyzes in detail the professional service process of Foshan multilingual website production company, covering key links such as demand analysis, multilingual adaptation, UI design, program development, etc., and compares the service differences in Dongguan, Zhongshan, Huizhou and other regions, providing a practical guide for enterprises to choose multilingual website construction services.![Cost and Benefit Analysis of Dongguan Multilingual Website Production Cost and Benefit Analysis of Dongguan Multilingual Website Production]() Cost and Benefit Analysis of Dongguan Multilingual Website ProductionThis article deeply analyzes the cost structure and commercial benefits of multilingual website production in Dongguan, compares the characteristics of service providers in the Pearl River Delta and major cities across the country, and provides companies with professional decision-making references for website internationalization construction.
Cost and Benefit Analysis of Dongguan Multilingual Website ProductionThis article deeply analyzes the cost structure and commercial benefits of multilingual website production in Dongguan, compares the characteristics of service providers in the Pearl River Delta and major cities across the country, and provides companies with professional decision-making references for website internationalization construction.![Huizhou multilingual website development, enhancing global competitiveness Huizhou multilingual website development, enhancing global competitiveness]() Huizhou multilingual website development, enhancing global competitivenessThis article details the importance and implementation strategies of Huizhou multilingual website development, covering the advantages, development process, key technologies, and success cases of multilingual websites to help enterprises enhance global competitiveness. It also provides professional recommendations for multilingual website production in Dongguan, Foshan, Zhongshan, Dalian, Zhengzhou, Shenzhen, Guangzhou, Beijing, and other locations.
Huizhou multilingual website development, enhancing global competitivenessThis article details the importance and implementation strategies of Huizhou multilingual website development, covering the advantages, development process, key technologies, and success cases of multilingual websites to help enterprises enhance global competitiveness. It also provides professional recommendations for multilingual website production in Dongguan, Foshan, Zhongshan, Dalian, Zhengzhou, Shenzhen, Guangzhou, Beijing, and other locations.![Foshan multilingual website production company customer case sharing Foshan multilingual website production company customer case sharing]() Foshan multilingual website production company customer case sharingThis article shares the successful customer cases of Foshan multilingual website production companies, and analyzes in detail the importance of multilingual website construction, technical implementation solutions, and how to enhance the international competitiveness of enterprises through professional services. It covers the multilingual website construction needs of enterprises in Dongguan, Zhongshan, Huizhou, Dalian, Zhengzhou, Shenzhen, Guangzhou, Beijing and other places, providing practical reference for enterprises interested in expanding overseas markets.
Foshan multilingual website production company customer case sharingThis article shares the successful customer cases of Foshan multilingual website production companies, and analyzes in detail the importance of multilingual website construction, technical implementation solutions, and how to enhance the international competitiveness of enterprises through professional services. It covers the multilingual website construction needs of enterprises in Dongguan, Zhongshan, Huizhou, Dalian, Zhengzhou, Shenzhen, Guangzhou, Beijing and other places, providing practical reference for enterprises interested in expanding overseas markets.
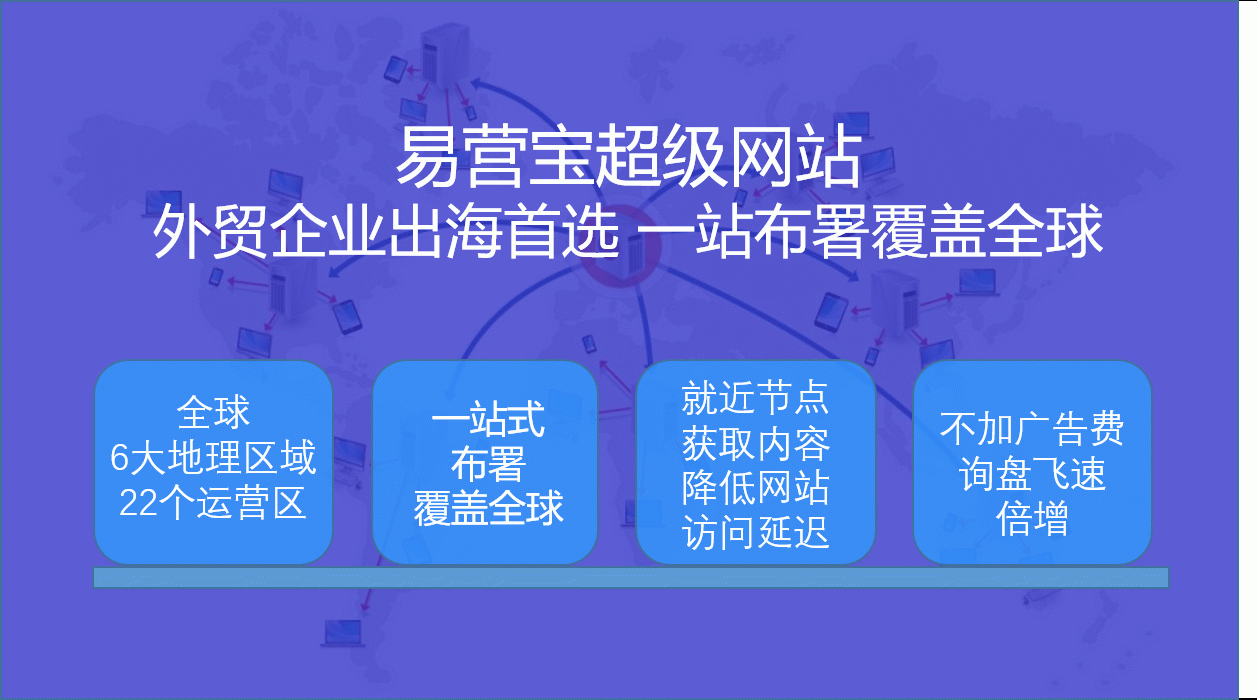
![EasyCampaign Foreign Trade Marketing (Super) Website EasyCampaign Foreign Trade Marketing (Super) Website]() EasyCampaign Foreign Trade Marketing (Super) WebsiteEasyCampaign Super Website, leveraging powerful global server networks and CDN acceleration services to ensure your website achieves lightning-fast access worldwide. This significantly enhances user experience, effectively improves website speed and retention rates, helping your business achieve global growth.
EasyCampaign Foreign Trade Marketing (Super) WebsiteEasyCampaign Super Website, leveraging powerful global server networks and CDN acceleration services to ensure your website achieves lightning-fast access worldwide. This significantly enhances user experience, effectively improves website speed and retention rates, helping your business achieve global growth.![EasyYun AI Translation Center EasyYun AI Translation Center]() EasyYun AI Translation CenterEasyYun AI Translation Center: Empowering multilingual standalone websites, enabling seamless global communication. Integrated with Google Neural Machine Translation technology, it generates multilingual websites with one click, achieving intelligent localization for foreign trade standalone sites and enhancing global market competitiveness.
EasyYun AI Translation CenterEasyYun AI Translation Center: Empowering multilingual standalone websites, enabling seamless global communication. Integrated with Google Neural Machine Translation technology, it generates multilingual websites with one click, achieving intelligent localization for foreign trade standalone sites and enhancing global market competitiveness.![Multilingual Website Solutions for Foreign Trade Multilingual Website Solutions for Foreign Trade]() Multilingual Website Solutions for Foreign TradeE-Yingbao SAAS Smart Website Builder offers precise translations in over 300 languages, overcoming language barriers for export businesses and boosting order conversion rates. Supporting all devices, global languages, SEO optimization, and omnichannel promotion, it empowers you to effortlessly expand into international markets.
Multilingual Website Solutions for Foreign TradeE-Yingbao SAAS Smart Website Builder offers precise translations in over 300 languages, overcoming language barriers for export businesses and boosting order conversion rates. Supporting all devices, global languages, SEO optimization, and omnichannel promotion, it empowers you to effortlessly expand into international markets.![B2B Foreign Trade Solutions B2B Foreign Trade Solutions]() B2B Foreign Trade SolutionsEasyTrade provides comprehensive services from foreign trade website construction to brand recognition, inquiry acquisition, and order fulfillment, helping foreign trade enterprises build high-conversion independent websites, obtain precise inquiries, establish international brand image, and accumulate private domain traffic.
B2B Foreign Trade SolutionsEasyTrade provides comprehensive services from foreign trade website construction to brand recognition, inquiry acquisition, and order fulfillment, helping foreign trade enterprises build high-conversion independent websites, obtain precise inquiries, establish international brand image, and accumulate private domain traffic.